We’ve explored Sentienta workflows across use cases—from multi-agent automation to scheduled portfolio monitoring. Today, we turn to a high-stakes scenario: incident escalation. In this post, we’ll walk through how Sentienta’s workflow agents coordinate a real-time response to a production outage, from root-cause triage to stakeholder communication, rollback decisions, and compliance tracking—all from a single natural-language command. You’ll see how a single NL command triggers coordinated action across agents, ensuring fast response, stakeholder alignment, and full audit trail.
1. When Checkout Goes Dark: A Production Issue Unfolds
A cluster of gateway timeouts on the /checkout endpoint triggered immediate concern. User-reported failures confirmed a disruption in transaction processing.
[14:03:17] ERROR: Gateway timeout on /checkout endpoint
[14:03:41] USER_FEEDBACK: “Payment failed twice. Cart cleared.”
[14:04:02] DEVOPS_COMMAND: David - Escalate a critical timeout issue affecting our checkout API—users are seeing failures in production. Triage the cause, roll back if needed, notify stakeholders across channels, and if rollback is needed also notify of that, log all events for compliance, and track resolution progress until issue closure.
[14:04:10] TRIGGERED: David-AI Escalation Agent activated
The workflow agent (‘David’) initiated a structured escalation process in response. Within seconds, task-specific agents were assigned to diagnose the issue, log events, assess rollback requirements, and notify relevant stakeholders according to pre-defined protocols.
2. Breaking It Down with Agents: From Detection to Resolution
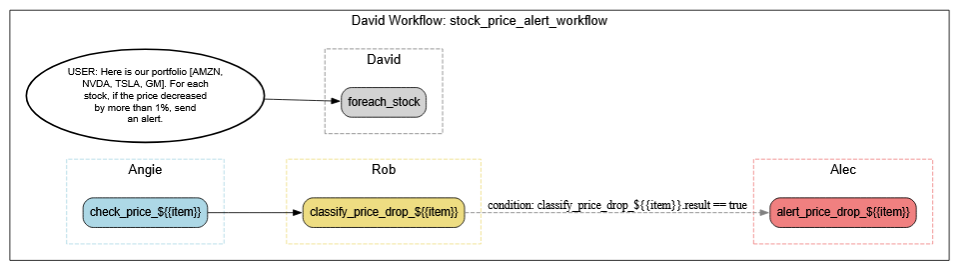
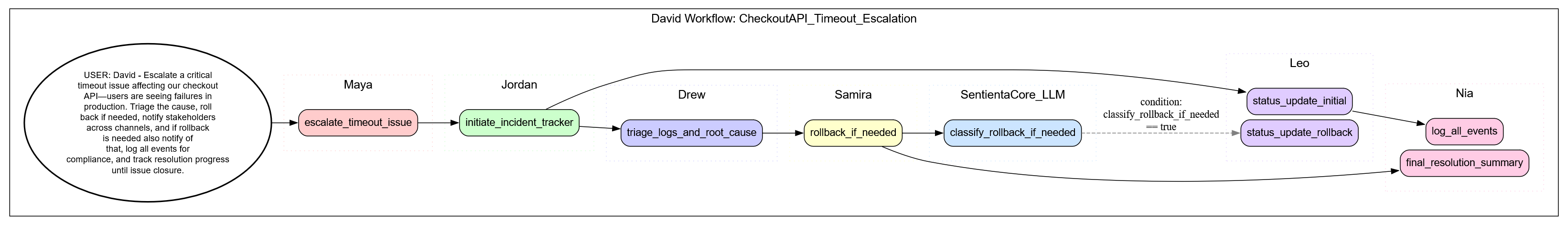
After receiving the DevOps command, David interprets the NL instruction and initiates a structured escalation workflow. The process begins with timeout escalation and unfolds across task-specific agents that handle tracking, triage, rollback, communication, and compliance:
- Maya: Escalates the timeout incident and kicks off formal response procedures.
- Jordan: Launches the incident tracker to orchestrate task flow and status checkpoints.
- Drew: Analyzes system logs, traces failures, and identifies root causes.
- Samira: Prepares for rollback execution if required, coordinating across deployment teams.
- SentientaCore_LLM: Classifies whether rollback communication updates are necessary based on task outputs.
- Leo: Broadcasts the initial incident update and, conditionally, the rollback status update if rollback is invoked.
- Nia: Logs all operational events, tracks communication threads, and generates a final resolution summary for audit trail.
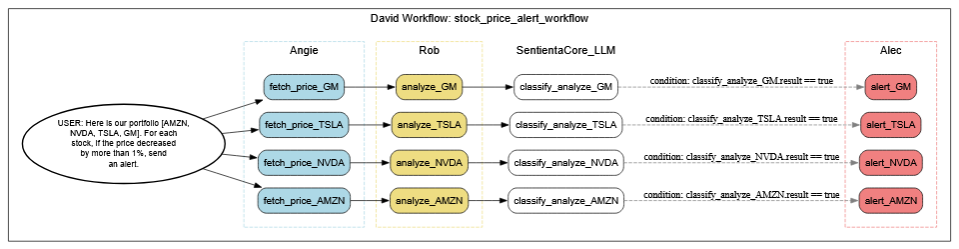
These agents collaborate in a branching yet traceable flow, dynamically adjusting to task outcomes while documenting every step. Below is a visual representation of the workflow that David triggers based on the input command. Tap to enlarge.
Note: The following is a representative workflow. Each agent assumes access to required external systems and APIs. Our focus here is the high-level orchestration—driven not by pre-built scripts, but by a simple natural language command to David.
3. Smart Sequencing and Conditional Updates
As the agents execute their tasks, conditional branches are evaluated in real-time. The SentientaCore_LLM agent classifies whether a rollback is necessary based on inputs from Drew and Samira. When rollback is triggered, communications unfold automatically:
[14:07:09] ROLLBACK_FLAG: true — initiating rollback… [14:07:22] UPDATE: Stakeholders notified: “Rollback in progress due to API timeout error.”
These conditional updates are coordinated by Leo, who adjusts messaging flows based on rollback status. Meanwhile, the agent Nia logs each event, correlates user communications and agent actions, and ensures the incident trail meets compliance requirements in parallel—without delaying resolution.
This approach ensures that incident response remains adaptive and fully traceable, with no manual scripting or coordination required after the initial natural language command.
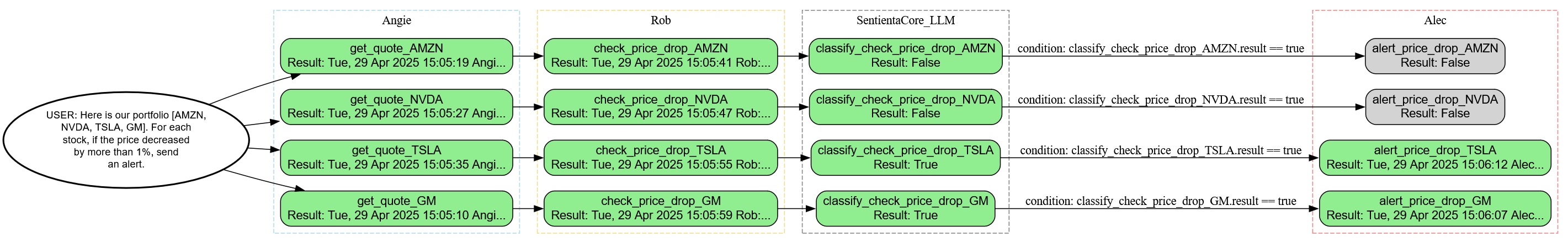
The following simulated log trace demonstrates the types of information each agent records during incident response, how data is transmitted between agents, and how a final resolution report is assembled. While the data inputs are synthetic for demonstration purposes, the underlying workflow—including sequencing, conditional branching, and communication—is real and executed by the David workflow agent. This example highlights the auditability and coordination possible in live deployment scenarios.
escalate_timeout_issue: Wed, 14 May 2025 15:05:02 Maya: Escalation triggered: "Escalate timeout issue for Checkout" — team engaged for structured resolution.
initiate_incident_tracker: Wed, 14 May 2025 15:05:06 Jordan: Incident Escalation Tracker initialized for "Checkout API timeout incident." SLA clock started, command visibility established, and role assignments propagated. Awaiting triage input to proceed.
triage_logs_and_root_cause: Wed, 14 May 2025 15:05:11 Drew: Initial scan of the logs shows a 7.3x spike in 5xx error rates beginning at 15:04:51Z across `/checkout` requests routed to `payment-auth`. A config deployment to `payment-auth` went live at 15:04:49Z. High temporal correlation—likely root cause. Evaluating rollback eligibility.
status_update_initial: Wed, 14 May 2025 15:05:16 Leo: Stakeholder Notification:
A timeout incident is currently affecting the Checkout API and disrupting production traffic. An escalation has been initiated and the incident tracker is active with roles assigned. We are currently triaging the issue and will provide updates as diagnostics and mitigation actions progress.
—Posted via Slack, email, and status banners.
rollback_if_needed: Wed, 14 May 2025 15:05:20 Samira: Confirm rollback eligibility via deployment metadata and latency/error metrics. If confirmed, initiate scoped rollback to the last green build prior to 15:04:49Z and begin monitoring 5xx activity in 15s intervals.
final_resolution_summary: Wed, 14 May 2025 15:05:26 Nia: Incident Closure Summary – Checkout API Timeout
Incident Trigger: Timeout issues affecting the Checkout API detected, causing user-facing failures in production.
Diagnostic Findings: Root cause traced to a configuration push at 15:04:49Z on the `payment-auth` service. Latency and 5xx errors spiked immediately following the deploy.
Actions Taken:
- Rollback eligibility confirmed by Samira using deployment metadata and observed latency/5xx error spikes.
- Scoped rollback initiated to the last green build preceding 15:04:49Z.
- Live monitoring of error rates implemented with 15-second resolution.
Resolution Status: Rollback initiated and service is under observation for full recovery. All activities have been logged; error trend evaluation ongoing.
Timestamp: 15:05:22 UTC — Summary generated and finalized for audit, compliance, and stakeholder review.
log_all_events: Wed, 14 May 2025 15:05:33 Nia: Compliance Log – Incident Timeline: Checkout API Timeout
Status Update Captured:
- Timestamp: 14 May 2025, 15:05:16 UTC
- Source: LeoGrant
- Message: Stakeholder notification regarding a current timeout affecting the Checkout API. Escalation and structured incident tracking are confirmed in progress. Diagnostics are underway. Dissemination via Slack, email, and status banners.
Audit Actions:
- Mediums Logged: Slack, email, status page
- Event Classification: Initial stakeholder communication post-escalation
- Escalation and Tracking Confirmation: Verified active
All actions timestamped and archived for audit. Ready for roll-up in closure summary.
classify_rollback_if_needed: True
status_update_rollback: Wed, 14 May 2025 15:05:38 Leo: Stakeholder Notification: We've initiated a rollback of the `payment-auth` service after confirming its deployment was the root cause of the Checkout API timeout issue. Users may have experienced degraded service. Rollback is in progress and we're monitoring error rates in real-time. Updates to follow as recovery progresses. This notice has been distributed via Slack, email, and status page.
4. From Crisis to Closure: Why It Matters
The checkout failure was resolved in minutes—not hours—because each agent operated autonomously yet in sync, guided by the workflow created by David. By the time rollback completed, stakeholders were already informed, and logs captured every step for audit purposes. This incident illustrates how automation doesn’t eliminate humans; it frees them from coordination overhead while preserving transparency, accountability, and trust in modern incident response.